Dubbo使用手册
官方网址:Apache Dubbo
什么是Dubbo?
Apache Dubbo 是一款易用的、提供高性能通信和服务治理能力的微服务开发框架,Dubbo 提供多种语言实现。
Dubbo中的应用、服务、方法
Dubbo 中有应用、服务和方法的概念。
- 一个应用可以发布多个服务
- 一个服务包含多个可被调用的方法
- 从抽象的视角来看,一次 Dubbo 调用就是某个消费方应用发起了对某个提供方应用内的某个服务特定方法的调用。
Dubbo基础架构
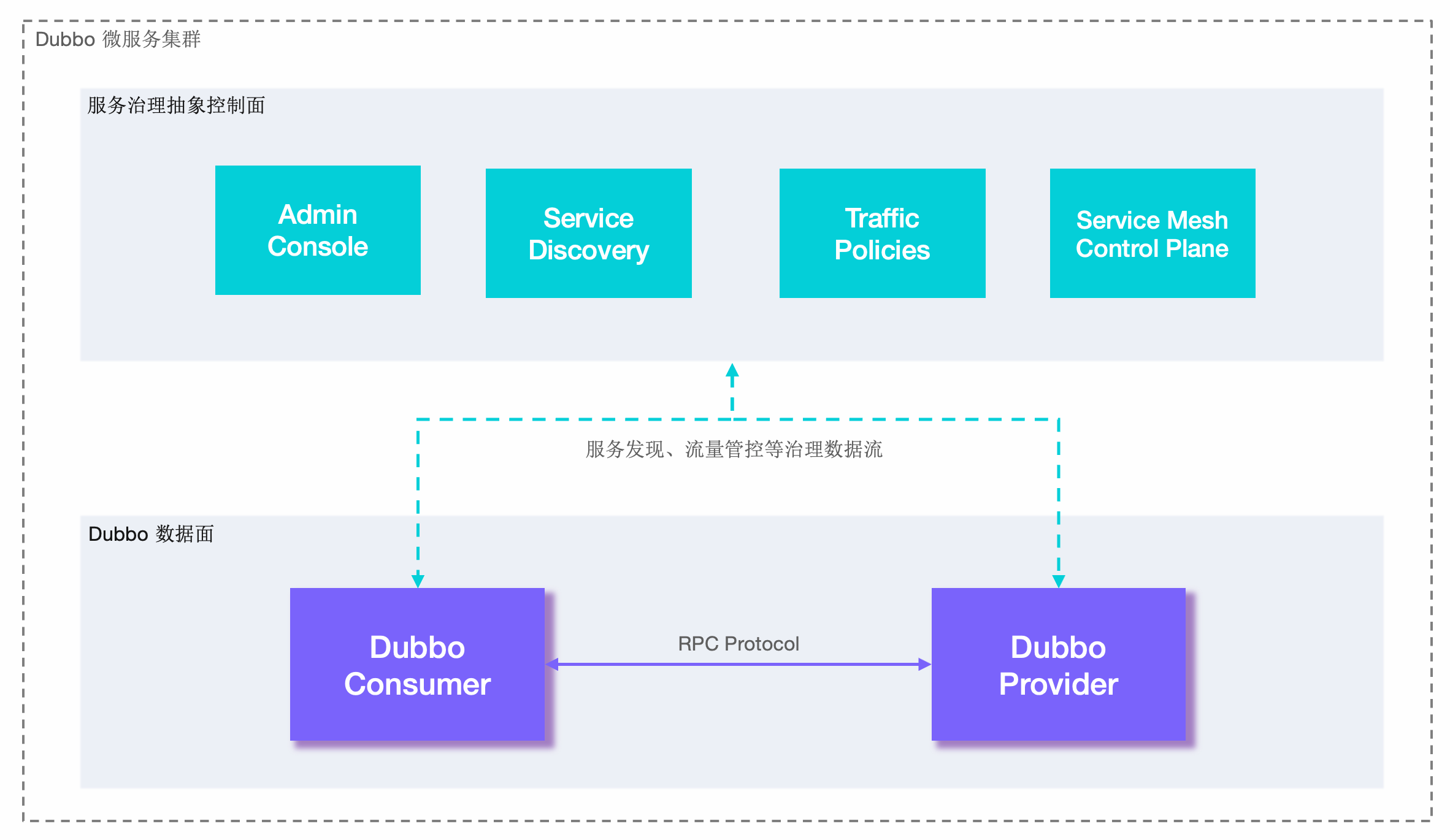
 Dubbo在架构图上分为两个部分:
Dubbo在架构图上分为两个部分:
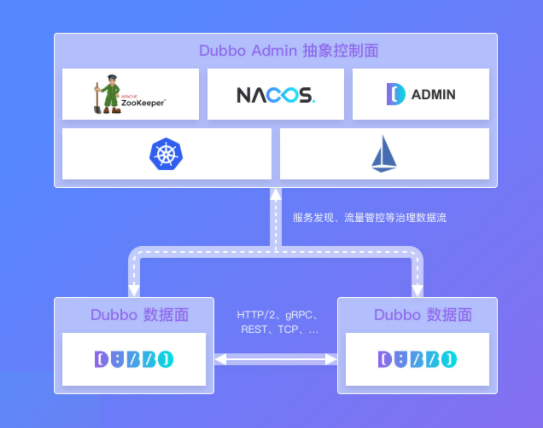
- 服务治理抽象控制面:DubboAdmin 控制面作为服务治理的抽象入口,由一系列可选的服务治理组件构成,负责 Dubbo集群的服务发现、流量管控策略、可视化监测。
- Dubbo数据面:在数据面,使用 Dubbo 开发的微服务进程间基于 RPC 协议通信
Dubbo服务治理
什么是服务治理?
在微服务集群环境下,我们需要解决无状态服务节点变化、外部化配置、日志跟踪、可观测性、流量管理、高可用性、数据一致性等一系列问题,这些问题统称为服务治理。
Dubbo提供的服务治理功能
- 地址发现
- 负载均衡
- 流量路由
- 链路跟踪
- 可观测性
Dubbo作为服务开发框架提供了哪些功能?
微服务开发
- RPC服务定义、开发范式:对各种开发,提供了服务定义和服务开发的范式。
- RPC服务发布与调用API:Dubbo支持同步、异步、流等服务调用编程模式。
服务发现
Dubbo引入注册中心,服务提供者向注册中心注册服务信息,服务消费者从注册中心订阅服务信息。
Dubbo2中的服务发现
在Dubbo2中,服务发现以接口粒度管理数据,服务提供者向注册中心注册详细的接口信息,包括服务地址、RPC元数据、RPC服务配置、RPC自定义元数据。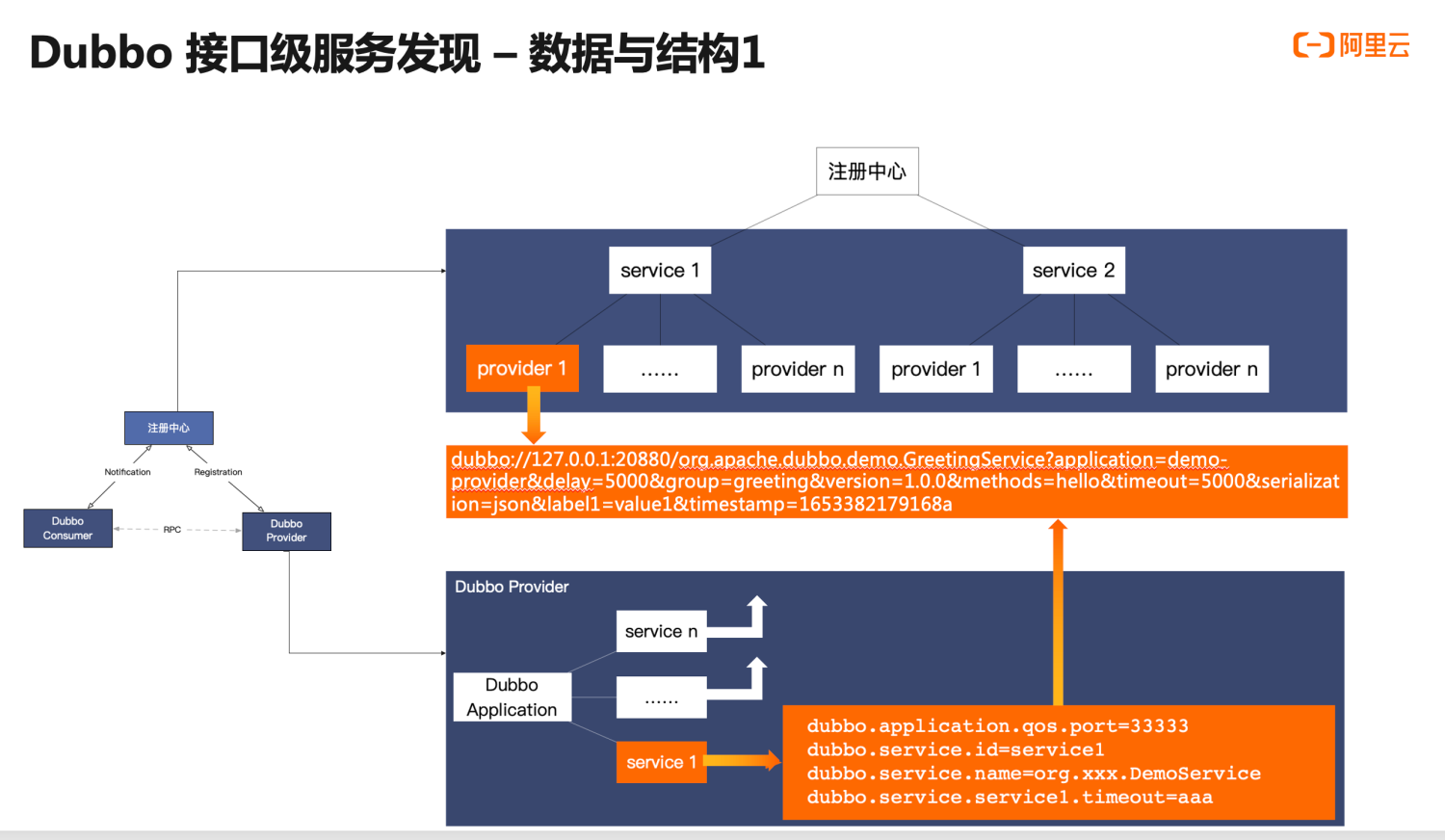 这种地址发现模型,为Dubbo带来了易用性、服务治理功能性、可拓展性的这些特点。但当集群节点数量增大到一定程序时,因为元数据信息占用了大量内存,反而影响到了业务功能。
这种地址发现模型,为Dubbo带来了易用性、服务治理功能性、可拓展性的这些特点。但当集群节点数量增大到一定程序时,因为元数据信息占用了大量内存,反而影响到了业务功能。
Dubbo3中的服务发现
在Dubbo3中,服务发现以应用粒度管理数据,服务提供者仅向注册中心注册服务ip和端口信息,注册中心以应用粒度聚合数据。服务消费者获取服务地址后,通过调用元数据服务,点对点地与服务提供者交换元数据信息。
负载均衡
Dubbo提供的是客户端负载均衡,即由客户端通过负载均衡算法确定将请求提交到哪个Provider实例。
负载均衡算法
| 算法 | 特性 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| Weighted Random LoadBalance | 加权随机 | 默认算法,默认权重相同 |
| RoundRobin LoadBalance | 加权轮询 | 借鉴于 Nginx 的平滑加权轮询算法,默认权重相同, |
| LeastActive LoadBalance | 最少活跃优先 + 加权随机 | 背后是能者多劳的思想 |
| Shortest-Response LoadBalance | 最短响应优先 + 加权随机 | 更加关注响应速度 |
| ConsistentHash LoadBalance | 一致性哈希 | 确定的入参,确定的提供者,适用于有状态请求 |
配置方式
Dubbo支持在服务提供者一侧配置默认的负载均衡算法,这样所有消费都将默认使用提供者指定的负载均衡算法。
消费者也可以自定义负载均衡算法。如果provider和consumer都没有提供,则使用默认的负载均衡算法。
同一个应用内支持配置不同的服务使用不同的负载均衡策略,支持为同一服务的不同方法配置不同的负载均衡策略。
流量管控
工作原理
Dubbo单个路由器的工作过程,路由器接收一个服务的实例地址集合作为输入,基于请求上下文(Request Context)和路由规则(Router Rule)对输入地址进行匹配,所有匹配成功的实例组成一个地址子集,最终地址子集作为输出结果继续交给下一个路由器或者负载均衡组件处理。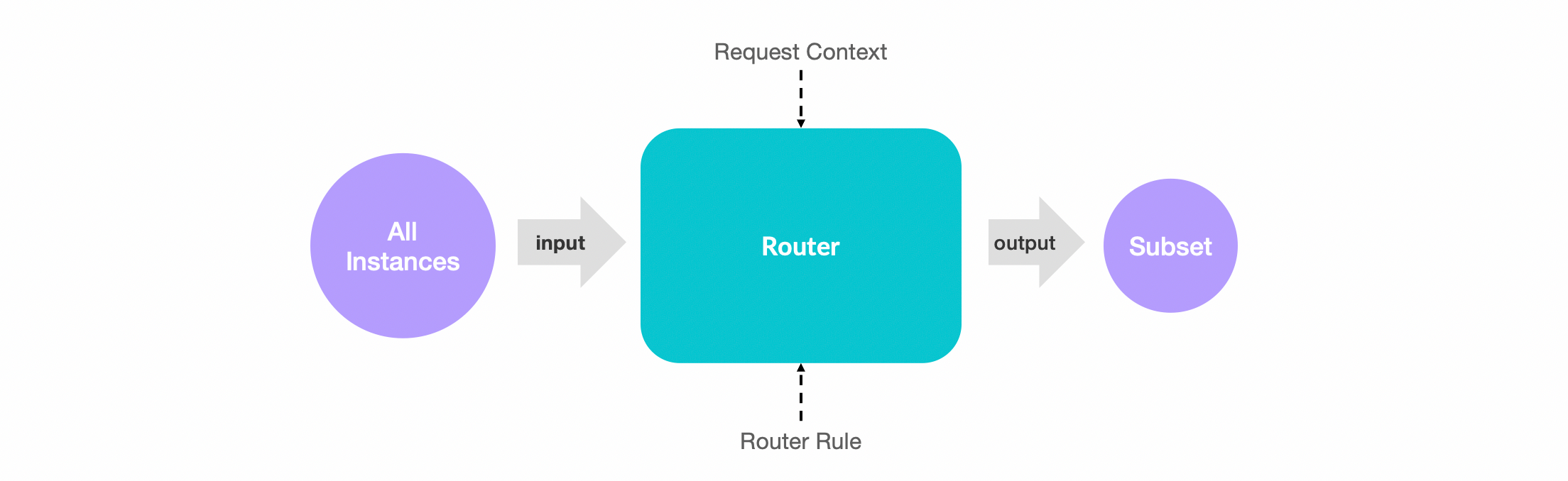

分类
Dubbo包含4种路由规则:
- 标签路由规则:tag标签,适用于应用维度。consumer的请求只会完全匹配对应标签的provider。
- 条件路由规则:conditions标签,适用于应用和服务维度。
- 脚本路由规则:scripts标签,灵活的配置,脚本路由只对消费者生效,在消费者端运行,适用于应用维度。
- 动态配置规则:通过dubbo-admin动态配置,适用于应用和服务维度。
条件路由实列
- 如果匹配条件为空,表示对所有请求生效,如:
=> status != staging - 如果过滤条件为空,表示禁止来自相应请求的访问,如:
application = product =>
configVersion: v3.0
enabled: true
force: false
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.CommentService
conditions:
- '=> region = $region'通信协议
Dubbo 框架不绑定任何通信协议,在实现上 Dubbo 对多协议的支持也非常灵活,它可以让你在一个应用内发布多个使用不同协议的服务,并且支持用同一个 port 端口对外发布所有协议。
Dubbo支持的RPC通讯协议
- Triple:是Dubbot3发布的云原生时代的通信协议,基于HTTP/2并且完全兼容gRPC,原生支持Streaming通信语义。
- Dubbo2:Dubbo2 协议是基于 TCP 传输层协议之上构建的一套 RPC 通信协议,Dubbo2时代被广泛使用。
- gRPC:gRPC 是谷歌开源的基于 HTTP/2 的通信协议
- Thrift:
- REST:
- ...
扩展适配
Dubbo的各语言的sdk实现都是采用”微内核+插件“的设计模式,几乎所有的流程中的核心节点都被定义为拓展点,通过扩展适配给用户带来最大的灵活性,同时提供了大量官方的组件拓展。 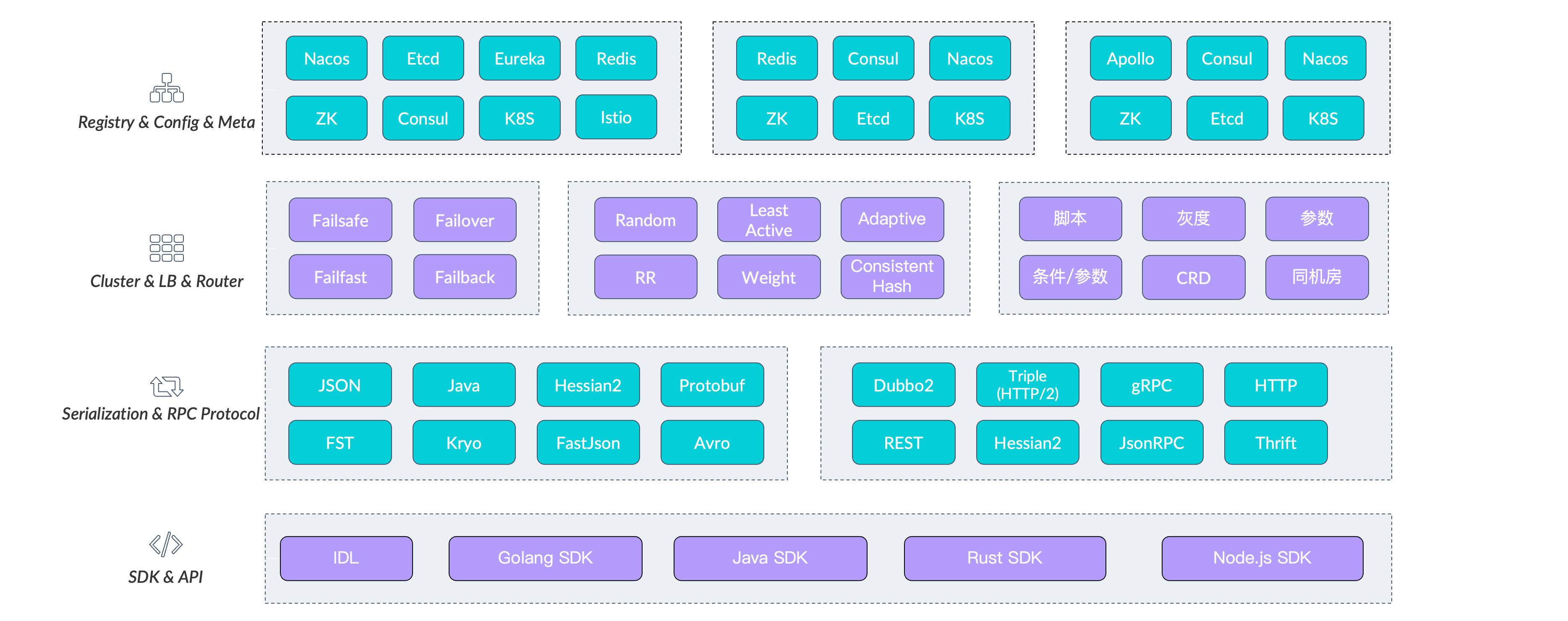 核心扩展点定义及实现,可分为3个层次展开:
核心扩展点定义及实现,可分为3个层次展开:
- 协议通信层
- 流量管控层
- 服务治理层
协议通信层
- Protocal:Protocol扩展点定义对应的是PRC协议
- Serualizaiton:Serialization扩展点定义了序列化协议扩展。
流量管控层
- Filter:流量拦截器
- Router:请求路由器
- Load Balance:负载均衡
- Cluster:集群故障转移
服务治理层
- Registry:注册中心是Dubbo实现服务发现能力的基础。
- Config Center:配置中心是用户实现动态控制Dubbo行为的关键组件。
- Metadata Center:元数据中心写入的是Dubbo实例的内部状态(如服务列表、服务配置、服务定义格式等),供一些治理能力作为数据来源。
观测服务
- ADMIN
- Metrics
- Tracing
- Logging
认证鉴权
Dubbo 提供了两种认证模式:
- 传输通道认证 (Channel Authentication)
- 请求认证 (Request Authentication)
Dubbo与Spring Cloud的关系
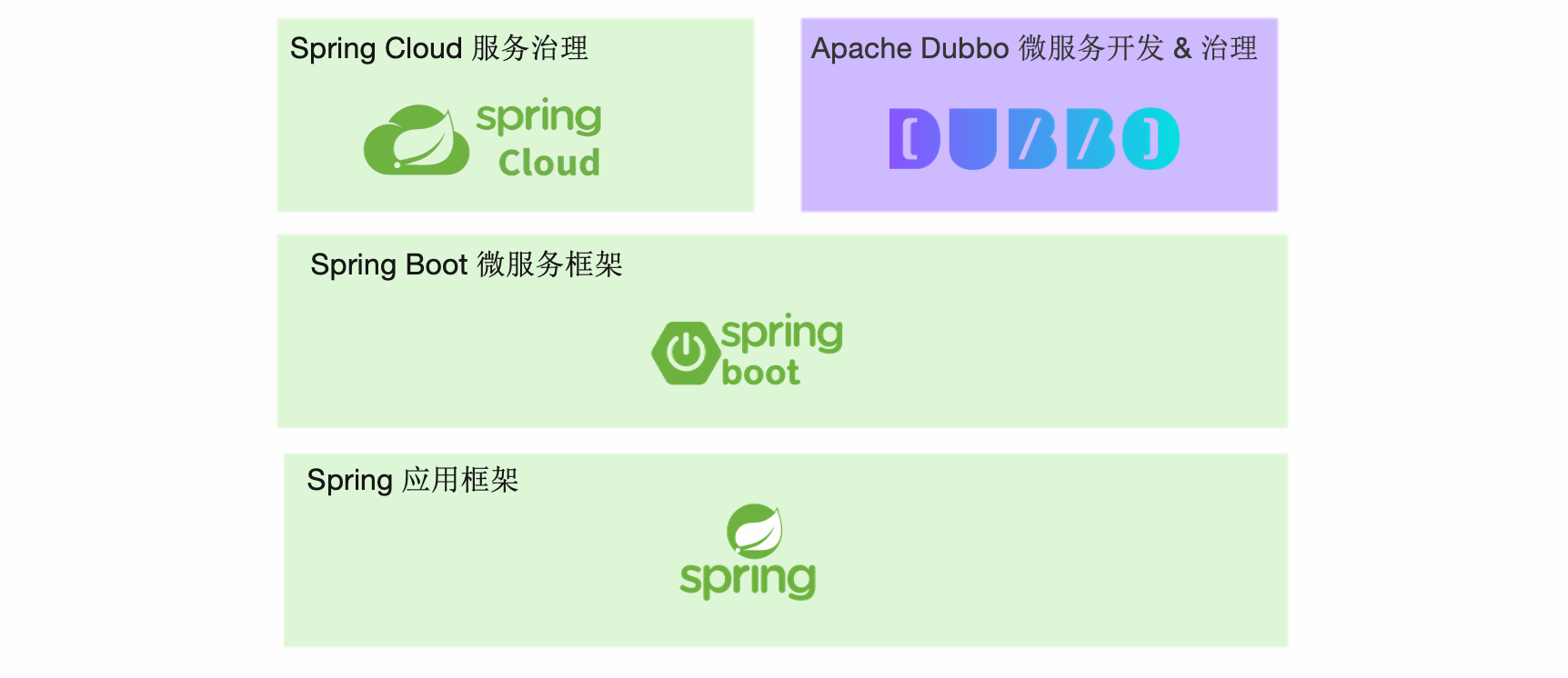 从官方的图中可以看出,Dubbo和Spring Cloud都是构建在Spring Boot之上,提供微服务治理的框架。但不同的是,Spring Cloud只提供了抽象模式的定义和简单的启动示例,在面对企业级生产环境时却有些无力,需要寻找类似的套件替代。而Dubbo提供了完整的实现方案,且提供了更出色的服务治理能力。
从官方的图中可以看出,Dubbo和Spring Cloud都是构建在Spring Boot之上,提供微服务治理的框架。但不同的是,Spring Cloud只提供了抽象模式的定义和简单的启动示例,在面对企业级生产环境时却有些无力,需要寻找类似的套件替代。而Dubbo提供了完整的实现方案,且提供了更出色的服务治理能力。
配置来源
Dubbo 默认支持 6 种配置来源:
- JVM System Properties,JVM -D 参数
- System environment,JVM进程的环境变量
- Externalized Configuration,外部化配置,从配置中心读取
- Application Configuration,应用的属性配置,从Spring应用的Environment中提取"dubbo"打头的属性集
- API / XML /注解等编程接口采集的配置可以被理解成配置来源的一种,是直接面向用户编程的配置采集方式
- 从classpath读取配置文件 dubbo.properties
注册中心
注册中心用于实现服务注册和服务订阅,可以设置一些参数。 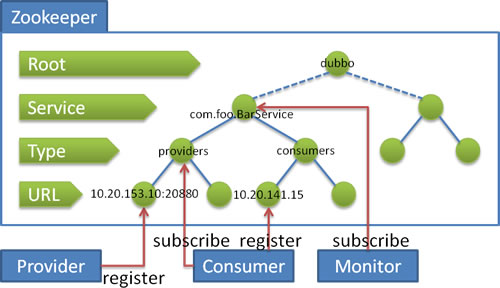
如果仅配置了注册中心的地址,在dubbo3中,会将注册中心也用于注册中心和元数据中心。
#单注册中心
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://${zookeeper.address:127.0.0.1}:2181
#多注册中心
dubbo.registries.beijing.address=10.20.153.10:2181,10.20.153.11:2181,10.20.153.12:2181
dubbo.registries.beijing.protocol=dubbo
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.address=zookeeper://10.20.153.10:2181?backup=10.20.153.11:2181,10.20.153.12:2181
#连接超时时间
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.timeout=6000
#会话超时时间
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.session=6000
#认证与鉴权
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.username=user
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.password=123456
#用于分组隔离
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.group=group1
#版本设置
dubbo.registries.hangzhou.version=v1.0配置中心
配置中心 (config-center) 在 Dubbo 中可承担两类职责:
- 外部化配置:启动配置的集中式存储 (简单理解为 dubbo.properties 的外部化存储)。
- 流量治理规则存储
Dubbo动态配置中心定义了两个不同层次的隔离选项,分别是namespace和group。
- namespace - 配置命名空间,默认值
dubbo。命名空间通常用于多租户隔离,即对不同用户、不同环境或完全不关联的一系列配置进行逻辑隔离,区别于物理隔离的点是不同的命名空间使用的还是同一物理集群。 - group - 配置分组,默认值
dubbo。group通常用于归类一组相同类型/目的的配置项,是对namespace下配置项的进一步隔离。如下图中的第3层的dubbo为分组全组配置,application为对应应用的配置。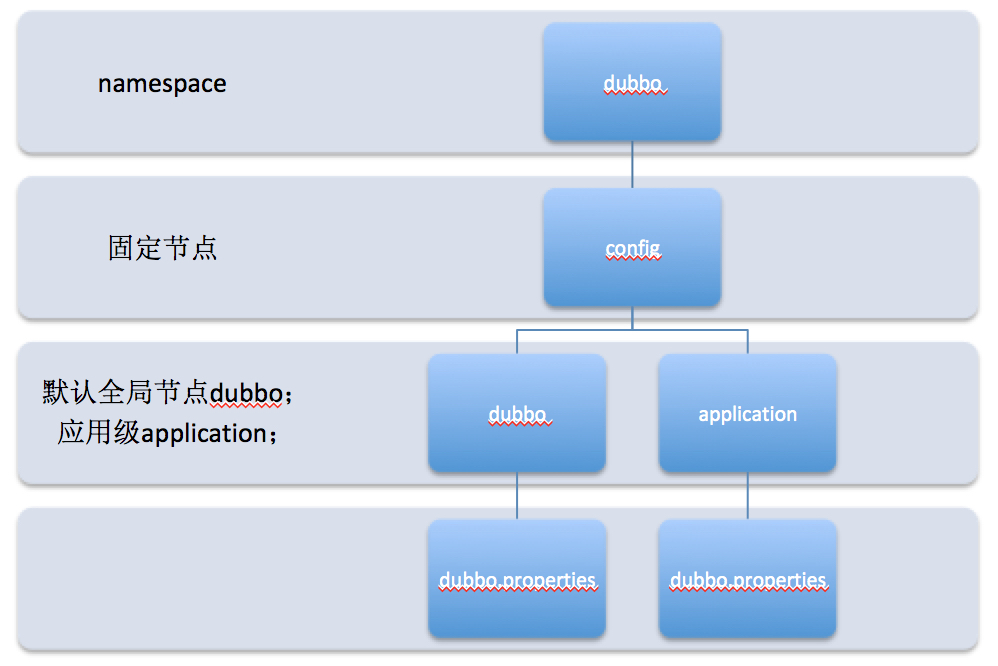
子节点除了dubbo.properties外,还存储了不同的服务治理规则,如configurators、tag-router、condition-router、migration等
元数据中心
Dubbo3中引入了应用级服务发现机制用来异构微服务体系互通与大规模集群实践的性能问题,应用级服务发现取代了Dubbo2时代的接口级服务发现。
Dubbo3围绕应用级服务发现引入了元数据机制,即 接口 - 应用映射关系 与 接口配置元数据,元数据中心包含了以上两类数据。
Dubbo Mesh

Docker安装Dubbo admin
1. 创建一个容器
$ docker run -p 38080:38080 --name dubbo-admin -d apache/dubbo-admin:0.5.02. 修改配置,保存与/config/application.properties
admin.registry.address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
admin.config-center: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
admin.metadata-report.address: zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181Java使用Dubbo
1. 启动一个注册中心。
Dubbo支持多种注册中心,包括:ZooKeeper、Nacos、Consul、Sofa、Polaris、Eureka、Etcd等。
2. 定义一个公共接口。
接口需要被服务提供端和服务消费端引用。
public interface GreetingService {
String sayHi(String name);
}3. 编写服务端功能
3.1 服务端实现公共接口
在服务提供端引入公共接口,并实现接口。
public class GreetingServiceImpl implements GreetingService {
@Override
public String sayHi(String name) {
return "Hi " + name;
}
}3.2 服务端定义服务信息
服务提供端使用ServiceConfig定义待发布服务的信息,setInterface设置服务的接口,setRef设置接口实现类的引用。
ServiceConfig<GreetingService> service = new ServiceConfig<GreetingService>();
service.setInterface(GreetingService.class);
service.setRef(new GreetingServiceImpl());3.3 服务提供端配置Dubbo启动器并启动
服务提供端使用DubboBootstrap配置Dubbo启动器,传入应用名、注册中心地址、协议信息以及服务信息等。注册中心地址、协议信息和服务信息可以传入多个。
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServiceConfig<GreetingService> service = new ServiceConfig<GreetingService>();
service.setInterface(GreetingService.class);
service.setRef(new GreetingServiceImpl());
DubboBootstrap.getInstance()
.application("first-dubbo-provide")
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.protocol(new ProtocolConfig("dubbo", -1))
.service(service)
.start()
.await();
}
}4. 编写服务消费端功能
4.1 引入公共接口,定义服务引用信息
ReferenceConfig<GreetingService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<GreetingService>();
reference.setInterface(GreetingService.class);4.2 服务消费端配置Dubbo启动器,获取服务,消费服务
服务消费端使用DubboBootstrap配置Dubbo启动器,传入应用名、注册中心地址以及服务引用信息等。注册中心地址、服务引用信息可以传入多个。
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ReferenceConfig<GreetingService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<GreetingService>();
reference.setInterface(GreetingService.class);
DubboBootstrap.getInstance()
.application("first-dubbo-client")
.registry(new RegistryConfig("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"))
.reference(reference);
GreetingService service = reference.get();
String message = service.sayHi("dubbo");
System.out.println(message);
System.in.read();
}
}5. 启动服务提供端和服务消费端
Spring集成Dubbo
1. 启动一个注册中心。
dubbo支持多种注册中心,根据需要引入相关依赖即可。
2. 定义公共接口
定义公共接口,供服务提供者、服务消费者引用
public interface DemoDubboService {
String sayHello(String name);
}3. 引入相关依赖
<!--dubbo-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>3.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.curator</groupId>
<artifactId>curator-x-discovery</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeeper</groupId>
<artifactId>zookeeper</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
</dependency>4. 编写服务提供者
4.1 服务提供者实现接口
public class GreetingServiceImpl implements GreetingService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}
}4.2 在Spring配置文件中定义Dubbo启动器和服务信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!--定义应用名-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-demo-provider"/>
<!--定义注册中心地址-->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<!--定义实现类对应的bean-->
<bean id="greetingService" class="com.chenzhuowen.springstudy.dubbo.provider.GreetingServiceImpl"/>
<!--定义服务信息,引用上面实现类的bean-->
<dubbo:service interface="com.chenzhuowen.springstudy.dubbo.api.GreetingService" ref="greetingService"/>
</beans>4.3 启动服务提供者
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("dubbo-demo-provider.xml");
applicationContext.start();
new CountDownLatch(1).await();
}
}5. 编写服务消费者
5.1 在Spring配置文件中定义Dubbo启动器和服务信息
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!--定义应用名-->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-demo-consumer"/>
<!--定义注册中心地址-->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>
<dubbo:reference id="greetingService" interface="com.chenzhuowen.springstudy.dubbo.api.GreetingService"/>
</beans>5.2 启动服务消费者
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:dubbo-demo-consumer.xml");
applicationContext.start();
GreetingService service = (GreetingService) applicationContext.getBean("greetingService");
String message = service.sayHello("dubbo");
System.out.println(message);
}
}SpringBoot集成Dubbo
SpringBoot下的简单使用
1. 启动一个注册中心。
dubbo支持多种注册中心,根据需要引入相关依赖即可。
2. 定义公共接口
定义公共接口,供服务提供者、服务消费者引用
public interface DemoDubboService {
String sayHello(String name);
}3. 引入相关依赖
服务提供者、服务消费者都需要引入相关依赖,这里引入了dubbo-starter和zookeeper的连接器。
<!-- Dubbo -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0-beta.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo to Zookeeper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo-dependencies-zookeeper-curator5</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0-beta.4</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- Dubbo to Nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.nacos</groupId>
<artifactId>nacos-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>4. 配置Dubbo启动器
在服务提供者、服务消费者的application.properties文件配置Dubbo启动器信息
#Dubbo配置
dubbo.application.name=dubbo-springboot-demo
dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo
#-1表示自动配置一个可用监听端口
dubbo.protocol.port=-1
dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://${zookeeper.address:127.0.0.1}:2181
#开启访问日志
dubbo.protocol.accesslog=true5. 定义服务
使用@DubboService注解类,表示类或方法,定义一个服务。
@DubboService
public class DubboProviderServiceImpl implements DemoDubboService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
}6. 消费服务
使用@DubboReference注解对象,引入一个服务。
@RestController
public class DubboConsumerController {
@DubboReference
DemoDubboService dubboService;
@GetMapping("/sayHello/{name}")
public String sayHello(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return dubboService.sayHello(name);
}
}Dubbo特性
Dubbo异步调用
Dubbo支持异步调用,Provider 端异步执行和 Consumer 端异步调用是相互独立的,你可以任意正交组合两端配置
- Consumer同步 - Provider同步
- Consumer异步 - Provider同步
- Consumer同步 - Provider异步
- Consumer异步 - Provider异步
上下文参数传递
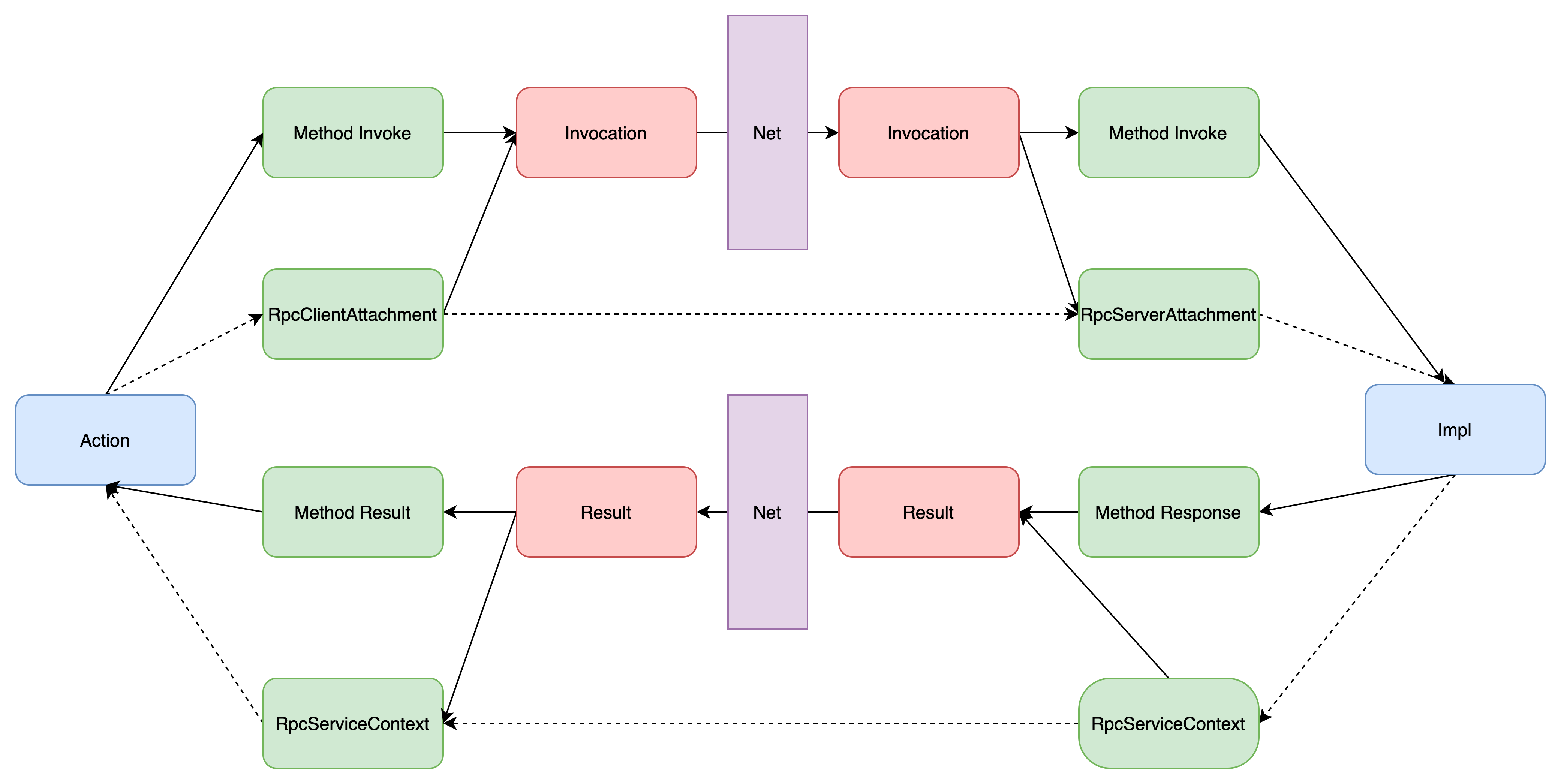
在Dubbo3中,RpcContext被拆分为四大模块(ServiceContext、ClientAttachment、ServerAttachment、ServerContext),可以使用Context传递参数或进行调用链路跟踪。
- ServiceContext:在Dubbo内部使用,用于传递链路上的数据。
- ClientAttachment:在Client端使用,往ClientAttachment中写入的参数会被传递到ServerAttachment中
- ServerAttachment:在Server端使用,通过ServerAttachment可以读取到从Client中传递过来的参数
- ServerContext:在Client端和Server端使用,用于Server端回传参数到Client端。ServerContext中的参数在调用结束后可以在 Client 端的 ServerContext 获取到。
path, group, version, dubbo, token, timeout 几个 key 是保留字段,请使用其它值。
setAttachment设置的 KV 对,在完成下面一次远程调用会被清空,即多次远程调用要多次设置。
参数透传是指参数可以在服务调用间传递。比如在服务A设置了参数,服务A调用服务B,服务B调用服务C,参数会从A传递到B,再从B传递到C。
为减少传递参数污染,Dubbo 3 对 RpcContext 进行了重构,支持可选参数透传,默认开启参数透传。
实现SPI接口PenetrateAttachmentSelector,可以自定义参数传递。
服务端
@DubboService
public class DubboProviderServiceImpl implements DemoDubboService {
final private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoDubboService.class);
@Override
public String contextInvoker(String param) {
Map<String, Object> objects = RpcContext.getServerAttachment().getObjectAttachments();
logger.info("ContextService serverAttachments:" + JSON.toJSONString(objects));
RpcContextAttachment serverContext = RpcContext.getServerContext();
serverContext.setAttachment("serverKey", "serverValue");
return "contextInvoker:" + param;
}
}客户端
@RestController
public class DubboConsumerController {
final private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemoDubboService.class);
@DubboReference
DemoDubboService dubboService;
@GetMapping("/contextInvoker/{name}")
public String contextInvoker(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
RpcContextAttachment clientAttachment = RpcContext.getClientAttachment();
clientAttachment.setAttachment("clientKey", "clientValue");
String res = dubboService.contextInvoker(name);
Map<String, Object> objects = RpcContext.getServerContext().getObjectAttachments();
logger.info("ContextService serverAttachments:" + JSON.toJSONString(objects));
return res;
}
}泛化调用
泛化调用(客户端泛化调用)是指在调用方没有服务方提供的 API(SDK)的情况下,对服务方进行调用,并且可以正常拿到调用结果。
//泛化调用
@GetMapping("/genericInvoker/{name}")
public String genericInvoker(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
ReferenceConfig reference = new ReferenceConfig();
reference.setInterface("com.chenzhuowen.springbootstudy.service.DemoDubboService");
reference.setGeneric("true");
ReferenceCache cache = SimpleReferenceCache.getCache();
GenericService genericService = (GenericService) cache.get(reference);
String result = (String) genericService.$invoke("sayHello", new String[]{"java.lang.String"}, new Object[]{name});
return result;
}控制台动态流量管控
流量管控
configVersion: v3.0
enabled: true
configs:
- addresses: [0.0.0.0] ## 0.0.0.0 for all addresses
side: provider ## effective side, consumer or addresses or provider
parameters:
timeout: 6000 ## dynamic config parameter
retries: 4
accesslog : true- address:配置会将规则发送到对应地址的应用
- side:
consumer配置会将规则发送到服务消费方实例。provider配置会将规则发送到服务提供方实例。 - timerout:动态配置超时时间
- retries:重试次数
- accesslog:开启服务提供方访问日志
条件路由
configVersion: v3.0
enabled: true
force: false
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.CommentService
conditions:
- '=> region = $region'- region:请求会优先发到相同区域的服务提供者
- force:这允许在同区域无有效地址时,可以跨区域调用服务
标签路由
configVersion: v3.0
force: true
enabled: true
key: shop-detail
tags:
- name: gray
match:
- key: env
value:
exact: gray- name:为灰度环境的流量匹配条件,只有请求上下文中带有
dubbo.tag=gray的流量才会被转发到隔离环境地址子集。 - match:指定了地址子集筛选条件,示例中我们匹配了所有地址 URL 中带有
env=gray标签的地址列表(商城示例中 v2 版本部署的实例都带已经被打上这个标签)。
参数路由
configVersion: v3.0
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.DetailService
scope: service
force: false
enabled: true
priority: 1
conditions:
- method=getItem & arguments[1]=dubbo => detailVersion=v2- method=getItem & arguments[1]=dubbo: 表示流量规则匹配
getItem方法调用的第二个参数,当参数值为dubbo时做进一步的地址子集筛选。 - detailVersion=v2: 将过滤出所有带有
detailVersion=v2标识的 URL 地址子集(在示例部署中,我们所有 detail v2 的实例都已经打上了detailVersion=v2标签)。
标签路由
configVersion: v3.0
scope: service
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.OrderService
configs:
- side: provider
match:
param:
- key: orderVersion
value:
exact: v2
parameters:
weight: 25标签orderVersion的值为v2的实例,权重设置为25。
多注册中心
服务分组
使用group属性,对同一个接口的不同实现进行区分
//提供者
@DubboService(group = "group1", version = "1.0")
public class DubboAsyncServiceImpl implements DubboAsyncService {
}
//消费者
@DubboReference(group = "group1", version = "1.0", check = false)
DubboAsyncService dubboAsyncService;线程池隔离
#当需要使用线程池隔离时,配置自定义的线程池
#thread pool management: default/isolation
dubbo.application.executor-management-mode=default
dubbo.provider.executor=自定以线程池名- default:使用原有以协议端口为粒度、服务间共享的线程池管理方式
- isolation:使用新增的以服务三元组为粒度、服务间隔离的线程池管理方式
executor参数只有指定dubbo.application.executor-management-mode=isolation时才生效。
是否注册服务
#true为注册服务到注册中心,false为不注册服务到注册中心,消费者可以使用直连方式调用服务
dubbo.registry.register=false消费者调用服务触发事件通知
消费者在消费者调用服务前、调用后、出现异常时,会触发oninvoke、onreturn、onthrow三个事件,可以配置当事件触发时,调用哪个方法。
<bean id ="demoCallback" class = "org.apache.dubbo.callback.implicit.NotifyImpl" />
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="org.apache.dubbo.callback.implicit.IDemoService" version="1.0.0" group="cn" >
<dubbo:method name="get" async="true" onreturn = "demoCallback.onreturn" onthrow="demoCallback.onthrow" />
</dubbo:reference>这几个调用事件绑定在服务的方法method下。事件触发时,执行的是bean的指定方法。
服务端对客户端进行回调
配合服务的method的callback属性使用
本地伪装
利用mock实现消费者调用服务,服务出错时的容错处理。
@DubboReference(check = false, mock = "force:return mock")
DemoDubboService dubboService;本地存根
在调用服务前执行一些动作,如做 ThreadLocal 缓存,提前验证参数,调用失败后伪造容错数据等等,此时就需要在 API 中带上 Stub,客户端生成 Proxy 实例,会把 Proxy 通过构造函数传给 Stud,然后把 Stub 暴露给用户,Stub 可以决定要不要去调 Proxy。
<dubbo:consumer interface="com.foo.BarService" stub="com.foo.BarServiceStub" />package com.foo;
public class BarServiceStub implements BarService {
private final BarService barService;
// 构造函数传入真正的远程代理对象
public BarServiceStub(BarService barService){
this.barService = barService;
}
public String sayHello(String name) {
// 此代码在客户端执行, 你可以在客户端做ThreadLocal本地缓存,或预先验证参数是否合法,等等
try {
return barService.sayHello(name);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 你可以容错,可以做任何AOP拦截事项
return "容错数据";
}
}
}实际上就是在远程代理对象上面,再加一层装饰。
回声测试
回声测试用于检测服务是否可用,回声测试按照正常调用执行,能够测试整个调用是否顺畅,亦可用于监控。
所有的服务自动实现EchoService接口,只需将任务服务引用强制转换成EchoService,即可使用。
//回声测试
@GetMapping("/echoService/{name}")
public String echoService(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
EchoService echoService = (EchoService) dubboService;
return (String) echoService.$echo(name);
}本地调用
当我们需要调用远程服务时,远程服务并没有开发完成,使用 injvm 协议在本地实现类似服务,调用此服务时可以调用我们本地的实现服务。
从 2.2.0 开始,每个服务默认都会在本地暴露。在引用服务的时候,默认优先引用本地服务。如果希望引用远程服务可以使用一下配置强制引用远程服务。
//在消费者端定义的本地injvm服务
@DubboService
public class DemoDubboServiceImpl implements DemoDubboService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "sayHello 本地";
}
@Override
public String contextInvoker(String param) {
return "contextInvoker 本地";
}
}如果在消费者中使用服务,会优先使用本地服务。
延迟暴露
在Dubbo2.6.5及以后版本,所有服务都将在Spring初始化完成后进行暴露,如果不需要延迟暴露服务,无需配置delay。
@DubboService(group = "group1", version = "1.0",delay = 2000)
public class DubboAsyncServiceImpl implements DubboAsyncService {
}只注册、只订阅
#只注册,subscribe属性表示,服务只注册到指定注册中心,不订阅注册中心的其他服务
dubbo.registry.subscribe=false
#只订阅,服务不注册到注册中心,但可订阅注册中心的其他服务
dubbo.provider.register=false分布式事务
在Dubbo中,可用采用Senta来完成分布式事务的支持。Senta分布式事务的原理是二阶段提交。